Das Hintergrundbeleuchtungssystem spielt eine große Rolle, wie ein Display aussieht und wie viel Energie es verbraucht. Als Schlüsselteil der LCDsEs hat einen starken Einfluss auf die Bildklarheit, den Energieverbrauch und die Schlankheit des Geräts. Lassen Sie’ Werfen Sie einen genaueren Blick auf sechs beliebte Hintergrundbeleuchtungstypen - CCFL, WLED, ELED, DLED, Mini LED und PWM - um mehr über ihre Grundlagen, Vorteile und Anwendungen zu erfahren.
CCFL
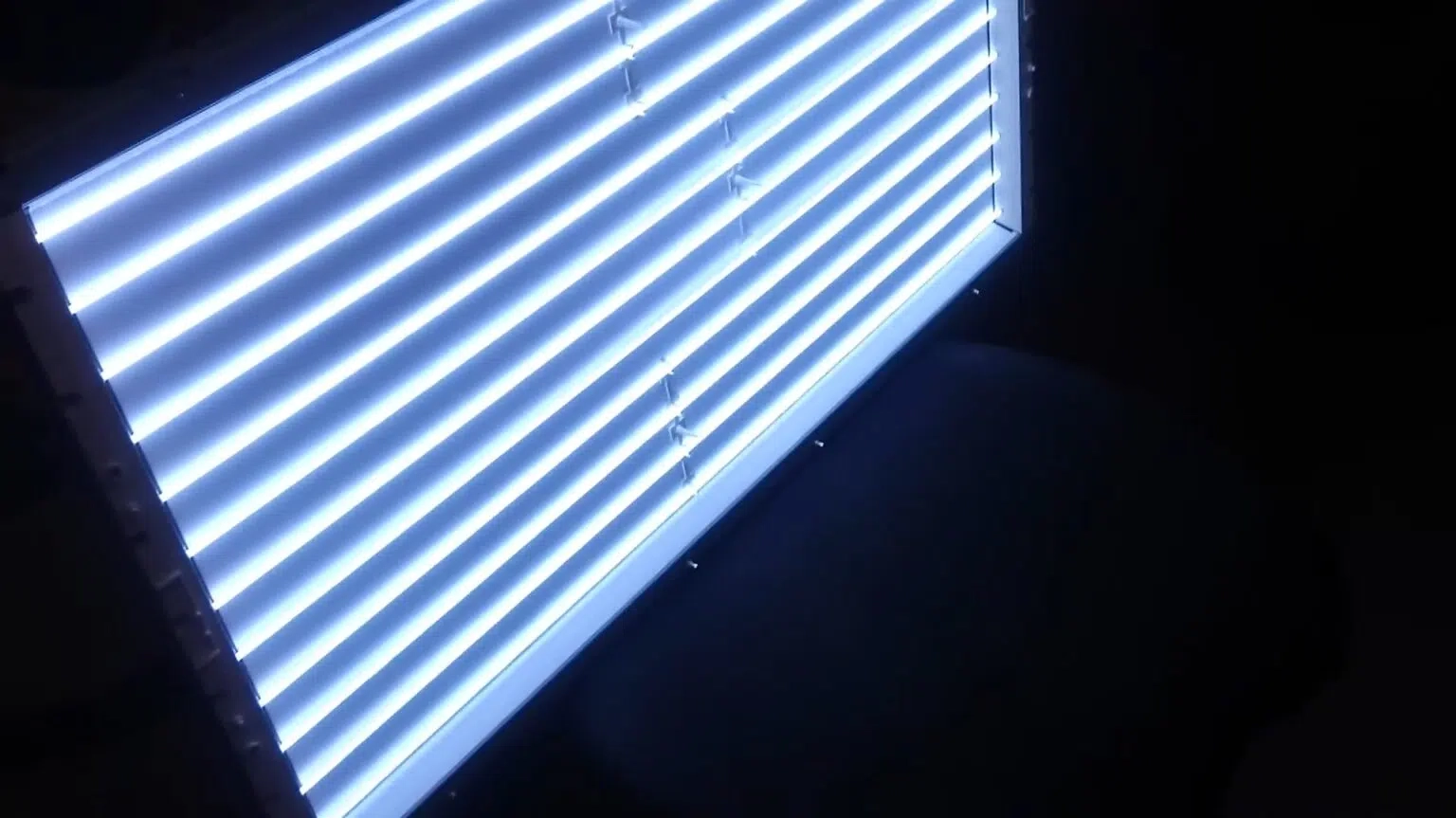

Grundprinzipien von Kaltkathoden-Leuchtstofflampen
Die frühe Hintergrundbeleuchtung Wahl war CCFL, oder kalte Kathode Leuchtstofflampen Röhren. Diese sehen sehr aus wie alte Leuchtstoffbirnen. Sie arbeiten, indem sie Quecksilberdampf aktivieren, um ultraviolette Strahlen abzugeben, die dann eine spezielle Beschichtung im Inneren des Rohres mit sichtbarem Licht leuchten lassen.
Struktur und Komponenten der CCFL-Hintergrundbeleuchtung
CCFL fällt unter rohrförmige Lichtquellen. Es erfordert eine komplizierte Einrichtung von Diffusorblättern und optischen Filmen, um das Licht gleichmäßig über den Bildschirm zu verteilen. Wenn die Bildschirme größer werden, werden mehr CCFL-Rohre benötigt, was das Design schwieriger zu verwalten macht.
Vorteile und Einschränkungen der CCFL-Technologie
CCFL bietet einen hellen, coolen Ton und ein anständiges Farbdisplay. Aber es kommt mit vielen Nachteilen. Es ist nicht sehr effizient, verbraucht mehr Energie, deckt nur einen kleinen Farbbereich ab (bis zu 72% NTSC), benötigt aufgrund der Rohrgröße einen dickeren Aufbau und weckt wegen Quecksilbers im Inneren Bedenken für die Umwelt.
Anwendungen und Markttrends für CCFL Displays
Aufgrund des hohen Energieverbrauchs und der Umweltschäden ist CCFL heute fast weg. Früher war es bei älteren LCD-Monitoren und Fernsehern üblich, aber jetzt haben LED-Optionen vollständig übernommen.
WLED
Wie weiße LED-Hintergrundbeleuchtung funktioniert
WLED steht für White Light Emitting Diode. Diese LEDs verwenden blaue Chips mit einer gelben Beschichtung oder eine Mischung aus Rot, Grün und Blau, um weißes Licht zu erzeugen. Dieses Licht verteilt sich gleichmäßig über LCD-Bildschirme.
Merkmale und Vorteile von WLED-Lösungen
Im Vergleich zu CCFL ist WLED ein großer Schritt nach vorne. Es ist jetzt die beste Wahl für die meisten LCD-Bildschirm-Hintergrundbeleuchtung. WLED bietet bessere Energieeinsparungen, schlankere Formen, schnellere Reaktion, längere Lebensdauer und ist freundlicher für den Planeten, da es kein Quecksilber enthält.
Effizienz und Farbpräzision in WLED-Displays
WLEDs ermöglichen eine bessere Kontrolle der Helligkeit und verbrauchen weniger Energie. Sie können eine breite Palette von Farben verarbeiten, was sie ideal für Gadgets wie Telefone und Tablets macht, die ein lebenswertes Farbdisplay benötigen.
Anwendungsfälle und Industrieanwendung von WLED
WLEDs beherrschen heute den Markt für Gadgets. Von Laptops bis hin zu Fernsehern und sogar industriellen Bildschirmen wie denen von Kadi Display, die unglaubliche Farben und solide Energieeinsparungen bieten, sind WLEDs sowohl für den Alltag als auch für erstklassige Anzeigebedarf.
ELED
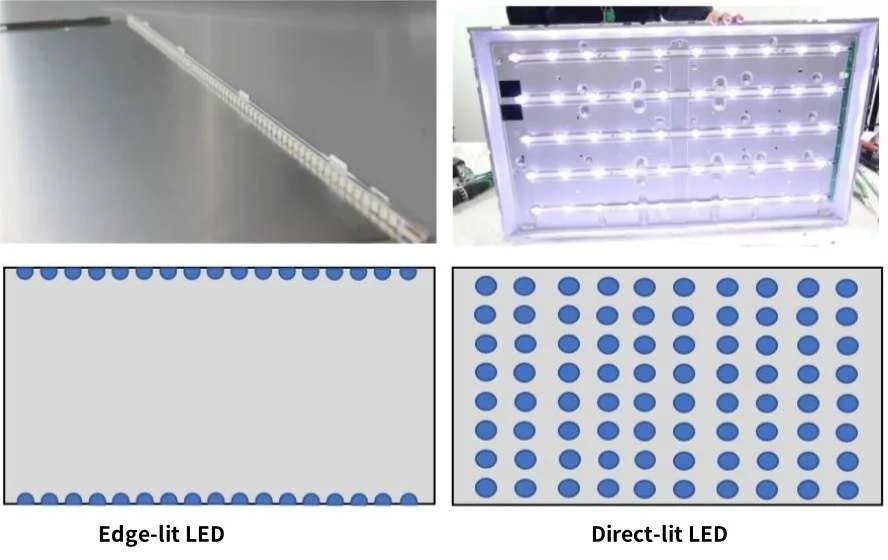
Verständnis der Edge-Lit LED-Technologie
ELED steht für edge-lit LED. Hier sitzen LEDs entlang der Seiten des Bildschirms. Eine spezielle Platte führt das Licht, um die gesamte Oberfläche gleichmäßig zu bedecken.
Konstruktionseigenschaften von ELED-Panels
Diese Einrichtung hilft, superdünne Bildschirme zu schaffen, da weniger LEDs rund um den Rahmen benötigt werden, als die gesamte Rückseite abdeckt. Deshalb funktioniert ELED gut für elegante Gegenstände wie Ultrabooks oder Fernseher an Wänden.
Leistungsvergleich mit anderen LED-Technologien
Während ELED-Bildschirme dünner sind als DLED-Bildschirme, müssen Unternehmen zusätzliche Anstrengungen unternehmen, um Helligkeit und Bildqualität zu verwalten. Wenn dies nicht richtig gemacht wird, kann dies zu ungleichmäßigem Licht oder einem schwächeren Kontrast führen.
Typische Anwendungen für ELED Displays
ELED erscheint oft in mittleren Fernsehern und Monitoren, wo ein schlanker Look wichtiger ist als ausgefallene Kontrastfunktionen. Sie werden es auch in erschwinglichen Signage für Unternehmen sehen.
DLED
Grundlagen der Direct-Lit LED-Hintergrundbeleuchtung
DLED steht für direct-lit LED. In diesem Stil werden LEDs gleichmäßig hinter dem Bildschirm platziert. Dadurch leuchtet die Hintergrundbeleuchtung gleichmäßig über das gesamte Display.
Strukturelle Unterschiede zwischen DLED und ELED
Im Gegensatz zu Edge-Beleuchtung Setups hat DLED LEDs direkt hinter dem Bildschirm. Dies macht das Panel dicker, ermöglicht aber eine bessere lokale Dimmung für scharfere Kontrastniveaus.
Helligkeit und Einheitlichkeit in DLED-Displays
DLED-Bildschirme bieten eine konstante Helligkeit über große Flächen. Sie bewältigen die Hintergrundbeleuchtung und die Bildqualität ziemlich gut, was sie zu einer guten Passform für die Darstellung von HDR-Inhalten macht.
Häufige Anwendungen in der Verbraucherelektronik
DLED ist ein Favorit für High-End-Fernseher, wo klare Bilder ein Muss sind. Es wird auch in Pro-Grade-Monitoren verwendet, wie die von Kadi Display, mit einer Helligkeit von über 1000nits für den Außenbereich oder schwierige industrielle Einstellungen.
Mini LED
Was unterscheidet Mini LED von herkömmlichen LEDs
Mini LED bezieht sich auf LEDs mit einer winzigen Chipgröße von 50-200μm. Diese kleinen Lichter lassen Hersteller Tausende in einen Bildschirm passen, im Gegensatz zu den Hunderten, die in älteren Designs verwendet werden.
Technische Spezifikationen und Konstruktionsüberlegungen
Die Zonen können von nur ein paar Hundert auf Tausende oder sogar Zehntausende springen. Dies ermöglicht eine genaue Dimmung in bestimmten Bereichen. Jede Zone entspricht mehreren Pixeln und erhöht den Dynamikbereich ohne Helligkeitsverlust.
Vorteile im Kontrastverhältnis und lokalen Dimmingzonen
Mit einer besseren lokalen Dimmung können Mini-LED-Hintergrundbeleuchtung-LCDs Kontrastverhältnisse über 1.000.000:1 erreichen. Dadurch können sie mit OLED-Bildschirmen konkurrieren und gleichzeitig die Verbrennungsprobleme mit organischen Materialien vermeiden.
Integration in moderne Display-Geräte
Mini-LEDs tauchen in ausgefallenen Tablets, Laptops und Gaming-Monitoren auf und erreichen Helligkeitsstufen von bis zu 3000 nits oder mehr. Aber billigere Mini LED-Bildschirme können einen Haloeffekt zeigen, wenn die Zonen nicht gut kontrolliert werden.
PWM
Die Rolle der Pulsbreitenmodulation bei der Hintergrundbeleuchtung
Die Pulsbreitenmodulation oder PWM verwendet Steuersignale, um die Helligkeit einer LED zu anpassen. Es tut dies, indem es das Licht schnell mit unterschiedlichen Geschwindigkeiten ein- und ausschaltet, was das menschliche Auge normalerweise nicht bemerken kann.
Wie PWM die Helligkeitsanpassung und die Energieeffizienz beeinflusst
PWM kann die Helligkeit der Hintergrundbeleuchtung LED auf der Fliege basierend auf dem, was auf dem Bildschirm ist ändern. Diese intelligente Einstellung spart bei dunklen Szenen Energie und schärft den Kontrast, den Sie sehen.
Potenzielle Probleme: Flickerwahrnehmung und Augenbelastungsrisiken
Selbst mit seinen Vorteilen kann PWM bei niedrigen Geschwindigkeiten ein Flimmern verursachen, was für einige Menschen zu Augenmüdigkeit oder Kopfschmerzen führt. Die Verwendung höherer Geschwindigkeiten kann dazu beitragen, dieses Problem sehr zu reduzieren.
Best Practices für die Implementierung von PWM in Displaysystemen
Für die besten Ergebnisse kann die lokale Dimmung in 1D-Licht (Randbeleuchtung) oder 2D-Licht (Direktbeleuchtung oder Mini LED) unterteilt werden. Der 2D-Typ liefert die scharfsten Bilder mit Kontrastverhältnissen von bis zu 500.000:1, wenn es richtig mit Mini- oder direktbeleuchteten LEDs gemacht wird.
FAQ (häufig gestellte Fragen)
F: Welche Hintergrundbeleuchtungstechnologie bietet den besten Kontrast?
A: Mini LED mit 2D lokaler Dimmung liefert den besten Kontrast, der bei richtiger Einrichtung über 1 Million:1 geht.
F: Wird CCFL heute noch verwendet?
A: Nein, es ist fast weg.
F: Was ist besser – ELED oder DLED?
A: Es hängt von der Verwendung ab. ELED ist schlanker, während DLED eine bessere Kontrolle über die Bildqualität bietet.
Holen Sie sich Ihre Anzeige Großhandel von Kadi Display: Beste China Display Monitor Fabrik
Kadi Anzeige bietet komplette Lösungen, einschließlich TFT-LCD-Module gepaart mit Touchscreens (CTP), PCBA-Boards und Gehäusen. Sie bieten auch kundenspezifische Optionen wie Schnittstellen (LVDS/MIPI/HDMI) und optische Verklebung mit OCA/OCR-Kleber für Zähigkeit.
Wir fertigen Cover Glas, um Ihren Bedürfnissen zu entsprechen - LOGO, Farbe, Form oder Dicke.
Wir passen FPCs, Kabel, Hintergrundbeleuchtung, Pinouts und Gehäuse genau darauf an, was Sie wollen.
Für zuverlässige hochhelle IPS TFT-LCDs mit bis zu 2500cd/m² Helligkeit garantiert Kadi eine klare Sichtbarkeit im Sonnenlicht und schnelle Reaktionszeiten mit AOI-geprüfter Produktion.
Schauen Sie sich unser breites Sortiment an, darunter robuste Industriemodule wie das "12.3" TFT-LCD-Modul mit hoher Helligkeit". Kontaktieren Sie unser Expertenteam noch heute!
Neueste Blog & Nachrichten
- How to Choose High Brightness LCD Displays for Outdoor Applications
- How to Choose the Best Industrial TFT LCD for Your Embedded Device
- IPS vs. andere Panels Wie man Displayschnittstellen für eingebettete und industrielle TFT-LCD auswählt
- 7-Zoll-MIPI-DSI-Displays: Top-Spezifikationen und beste Auswahl im Jahr 2026
- Wide Temperatur TFT Displays für industrielle Anwendungen