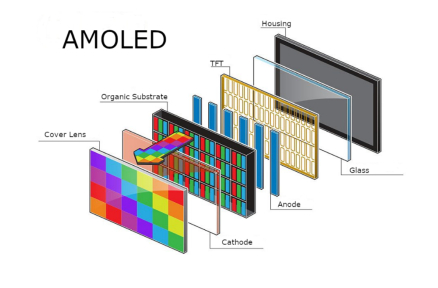
Что такое дисплейный интерфейс?
Для целей отображения контроллер отображения обеспечивает интерфейс между мультимедийным процессором и модулем отображения. В основной логике интерфейс отображения является средством передачи сигналов главного контроллера в модуль отображения. В Дисплей TFT модуль, интерфейс обычно приходит вместе в FPC или PCB, и даже в расширении ЖК-контроллеров.
Выбор подходящего интерфейс дисплея Важно для обеспечения совместимости и производительности между процессором вашей системы и его визуальным выходом. Выбранный тип интерфейса влияет не только на разрешение и размер, но и на потребление энергии, скорость и сложность.
6 наиболее распространенных типов TFT-дисплейных интерфейсов
В соответствии с режимом управления TFT-ЖК основные типы интерфейса входа сигнала являются следующими: MCU (также известный как MPU), SPI, TTL (также известный как RGB), LVDS, DSI (также известный как MIPI) и EDP.
MCU (микроустройство управления)
Основная архитектура и рабочий принцип
Интерфейс MCU имеет важное значение, поскольку он может записывать и читать данные, хранящиеся во внутреннем буфере кадров или хранилище гаджета. Как правило, он поддерживает небольшие дисплеи менее 5 дюймов с разрешением ниже 480× 800.
Каждый интерфейс MCU включает в себя четыре типа сигналов: RD (читать сигнал включения в интерфейсе MCU 8080), WR (записывать сигнал включения в интерфейсе MCU 8080), RS (перезагрузить штрих), CS (выбрать штрих чипа), сигналы данных: 18-битный, 16-битный, 9-битный или 8-битный
Преимущества и ограничения
Интерфейсы MCU просты в реализации и экономически эффективны. Однако у них отсутствует высокоскоростная производительность, что делает их непригодными для больших или высоких дисплеев разрешения.
Типичные случаи использования во встроенных системах
Этот тип идеально подходит для встроенных систем с низкой мощностью, таких как портативные счетчики или основные пользовательские интерфейсы на приборах.
SPI (серийный периферический интерфейс)

Обзор протокола связи
SPI - это интерфейс серийного периферического устройства. Он выполняет синхронную последовательную передачу данных между процессором и IC драйвера. Данные передаются в битах, с высокими битами спереди и низкими битами сзади.
Он поддерживает как 3-строчные, так и 4-строчные конфигурации в зависимости от требований к конструкции.
Преимущества SPI в дисплейных приложениях
SPI требует меньшего количества штифтов, чем параллельные интерфейсы, что уменьшает сложность PCB. Это’ подходит для компактных устройств, где экономия места имеет решающее значение.
Соображения по производительности
Скорость передачи составляет всего несколько Мбит/с, что медленно. Поэтому это’ обычно используется для дисплеев с низким разрешением, таких как те, которые находятся в умных носимых устройствах или небольших домашних устройствах.
TTL-RGB (транзисторная логика транзистора – красный зеленый и синий)
Механизм передачи сигнала
Сигнал уровня TTL генерируется устройством TTL. Интерфейс TTL передает данные параллельно. Он накладывает изменения трех цветовых каналов красного (R), зеленого (G) и синего (B) и выходит их вместе.
Конфигурация Pin и электрические характеристики
Каждый интерфейс RGB включает в себя пять типов сигналов: VS (вертикальная синхронизация), HS (горизонтальная синхронизация), DCLK (точечные часы), DE (включение данных), D0…DXX
Интерфейсы RGB могут варьироваться от 6-битного до 24-битного в зависимости от требований к глубине цвета.
Сценарии применения
Интерфейсы TTL-RGB широко используются в средних дисплеях, требующих быстрых обновлений, таких как воспроизведение видео, обычно встречающихся в автомобильных приборных панелях или промышленных панелях HMI.
MIPI-DSI (Мобильный Процессорный Интерфейс – Серийный Интерфейс Дисплейа)
Высокоскоростные функции серийной связи
DSI - это серийный интерфейс дисплея, который является стандартным интерфейсом дисплея, определенным MIPI Alliance. Его преимуществами являются более низкое потребление энергии, более высокая скорость передачи данных (около 1 Гбит/с) и меньшее пространство для размещения.
Он поддерживает несколько полос - от 1 до 8 - для масштабирования пропускной способности на основе потребностей в разрешении.
Энергоэффективность и пропускная способность данных
MIPI-DSI обеспечивает отличную энергоэффективность при сохранении высокой пропускной способности. Особенно полезно для мобильных устройств, работающих на батареях.
Использование в мобильных и компактных устройствах
Следовательно, интерфейс применяется в основном к терминалам, которые требуют дисплеев высокого разрешения, таких как планшеты, смартфоны и ноутбуки.
LVDS (дифференциальная сигнализация низкого напряжения)
Технология дифференциальной сигнализации объясняется
Интерфейс LVDS представляет собой технологию дифференциального сигнала с низким колебанием. Он может сделать передачу сигнала со скоростью сотен Мбит/с на дифференциальной паре линий или сбалансированном кабеле
LVDS использует сигнализацию, управляемую током, с каянием ±350 В при уровне смещения постоянного тока 1,2 В.
Шумный иммунитет и целостность сигнала
Мешания между одной и той же парой дифференциалов и линий могут отменить друг друга, поэтому антимешальная способность сильна.
Это делает LVDS очень подходящим для промышленных сред с электрическим шумом.
Реализация в промышленных дисплеях
10,1-дюймовый IPS 1920 × 1200 TFT ЖК-дисплей с интерфейсом LVDS, 12,1-дюймовый 1024 × 768 TFT ЖК-дисплей с интерфейсом LVDS являются примерами, используемыми в промышленных приложениях, требующих стабильной производительности в суровых условиях.
EDP (встроенный порт дисплея)
Интеграция с современными графическими процессорами
Интерфейс EDP представляет собой цифровой интерфейс, основанный на архитектуре и протоколе порта дисплея. Он позволяет прямую интеграцию в графические процессоры, обычно встречающиеся в ПК или встроенных вычислительных платформах.
Возможности пропускной способности и поддержка разрешения
Он может передавать сигналы высокого разрешения с помощью более простых разъемов и меньшего количества штифтов, поддерживая разрешения далеко за пределами Full HD без необходимости в нескольких полосах, как LVDS.
Подходит для высококачественных дисплеев
15,6-дюймовый 3840×2160 AM-OLED EF60UBA68 иллюстрирует, как eDP поддерживает доставку контента ультравысокого разрешения для премиум-мониторов или потребительской электроники, таких как ноутбуки.
Сравнение всех 6 интерфейсов
| Интерфейс | Скорость | Количество Pin | Приложение | Поддержка резолюции |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| МКУ | Низкий | Средний | Малые экраны (<5") | До 480× 800 |
| СПИ | Низкий | Низкий | Носимые устройства/IoT | Ниже 320× 480 |
| TTL-RGB | Средний | Высокий | Средние дисплеи/воспроизведение видео | До WXGA |
| MIPI-DSI | Высокий | Низкий | Смартфоны/планшеты/ноутбуки | До UHD |
| LVDS | Высокий | Средний | Промышленные/автомобильные дисплеи | До WUXGA |
| eDP | Очень высокий | Низкий | ПК/высококачественные мониторы/ноутбуки | За пределами UHD |
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Какой дисплейный интерфейс я должен использовать для носимых устройств?
Используйте SPI из-за его минимальных требований к количеству штифтов, подходящих для небольших форм-факторов.
MIPI лучше LVDS?
MIPI имеет более высокую энергоэффективность, но требует более сложной инициализации; LVDS предлагает надежную целостность сигнала, идеальную для промышленного использования.
Могу ли я конвертировать между интерфейсами?
- Да. - Да. Для размещения различных сигналов из-за ограничений драйвера, ему нужен дополнительный ЖК-преобразователь или плата контроллера ... обычное преобразование, такое как RBG в LVBS, VGA, CVBS
Получите свой дисплей оптом от Kadi Display: лучший Китай дисплей монитор фабрики
В более чем 20 лет опыта в отрасли дисплея, мы обнаружили, что большое количество клиентов нуждаются не только в TFT-ЖК, но и в полном решении дисплея, интегрирующем сенсорный, PCBA и корпус. Кади Дисплей имеет фабрику площадью более 5000 квадратных метров. Ванна Дисплей имеет профессиональную R& Команда D отвечает за платы адаптеров сигнала.
Независимо от того, нужны ли вам настройки FPC/кабелей/интерфейсов, таких как TTL/LVDS/MIPI/EDP/HDMI/VGA/USB-A, Kadi Display предлагает индивидуальные решения, которые сокращают время разработки, одновременно повышая уникальность продукта.
Исследуйте наши предложения, включая 12,3-дюймовый TFT-LCD модуль с интерфейсом LVDS высокой яркостью, 10,1-дюймовый TFT-LCD с интерфейсом CTP LVDS или даже AMOLED, такие как 7,0-дюймовый с интерфейсом MIPI 1080 × 1920 AMOLED. Свяжитесь с нашей командой экспертов сегодня!
Последние блоги и новости
- How to Choose High Brightness LCD Displays for Outdoor Applications
- How to Choose the Best Industrial TFT LCD for Your Embedded Device
- IPS против других панелей Как выбрать интерфейсы дисплея для встроенного и промышленного TFT-ЖК
- 7-дюймовые дисплеи MIPI DSI: лучшие спецификации и лучший выбор в 2026 году
- Широкотемпературные TFT-дисплеи для промышленных приложений
Блог и новости
-
TN против IPS2024-7-9
-
TN против IPS2024-7-9