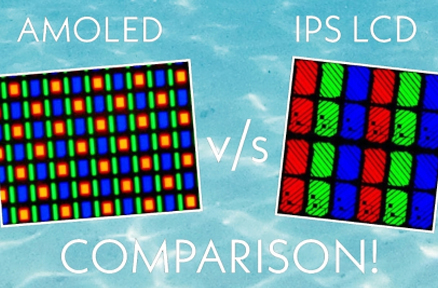
Понимание технологии: ЖК и OLED дисплеи
Технология экрана является основной частью сегодняшнего’ с гаджетами. LCD и OLED являются наиболее распространенными вариантами. А ЖК-экран работает с помощью жидких кристаллов для управления светом, который поступает от подсветки, обычно изготовленной из светодиодов. Необходимы поляризационные фильтры и цветовые фильтры для фотографии. Такой способ гибкий для многих размеров и мест.
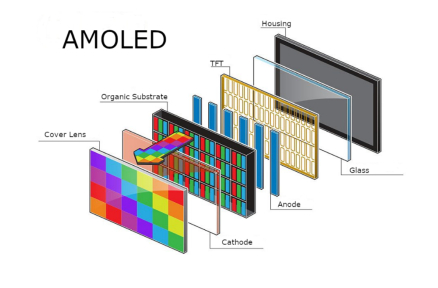
С другой стороны, OLED использует специальные органические материалы, которые сами выделяют свет, когда через них проходит электричество. Нет необходимости в подсветке. Каждый пиксель работает самостоятельно. Это означает, что каждый из них может сиять или оставаться темным отдельно. Это дает точный контроль над яркостью и цветом.
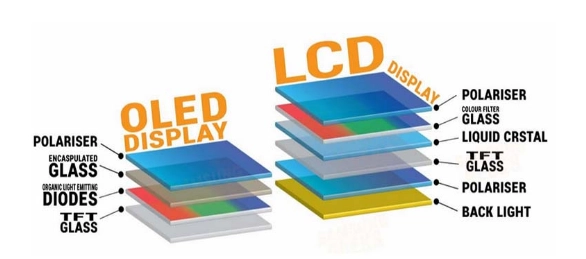
Некоторые основные особенности делают их разными в реальном использовании. ЖК-экраны дешевле и отлично работают в ярком солнечном свете. Они используют меньше энергии, когда картина в основном яркая. Это делает их хорошими для наружных фабричных панелей или приборных панелей автомобилей. Они также остаются сильными в тяжелую погоду. Они могут справляться с температурами от -30°C до 85°C без проблем.
OLED экраны дают гораздо лучший контраст, потому что каждый пиксель освещается сам. Они показывают настоящий черный цвет и сохраняют цвета стабильными даже когда вы смотрите со стороны, до 178 градусов. Пиксели работают быстро. Это помогает быстро движущимся медицинским снимкам или игровым экранам, которые часто обновляются.
Как они построены также меняет, насколько хорошо они работают. Для ЖК, тип подсветки имеет большое значение. Некоторые используют краевое освещение, другие используют полномасштабное локальное затемнение (FALD). То, как жидкие кристаллы выстраиваются, тоже важно. Специальные яркие модели могут достигать 1100 нитов. Это помогает людям четко видеть даже на прямом солнце.
Для OLED все зависит от того, насколько стабильны органические материалы и как расположены пиксели. Новые версии могут изгибаться, поэтому возможны изогнутые экраны. Оба типа становятся лучше. ЖК уже очень зрел, поэтому крупные заводы могут легко зарабатывать миллионы. OLED приносит свежие идеи и остается на высоком рынке.
Оценка качества изображения: LCD vs OLED
Качество изображения – это первое, что проверяет большинство людей. Она включает в себя остроту, детали и то, как все выглядит реально. OLED-экраны дают удивительную глубину, потому что их контраст почти идеален. Пиксели могут полностью отключаться для чистого черного. Это хорошо выглядит в темных видео безопасности или медицинских фильмах. Вокруг ярких пятен почти нет утечки света. ЖК-экраны всегда включают подсветку. Их черные области выглядят более серыми. Тем не менее, новые мини-светодиодные фонари очень помогают. Они отключают небольшие зоны и делают средние тоны выглядят лучше.
Цвета выглядят более живыми и на OLED. Они покрывают более 100% DCI-P3. Это означает, что цвета кажутся очень богатыми и близкими к реальной жизни. Это помогает дизайнерам или врачам, которым нужны точные цвета. Иногда цвета могут выглядеть слишком сильными, поэтому необходима калибровка. ЖК-экраны дают естественные и сбалансированные цвета, особенно с обновлениями квантовых точек. Их цветовой диапазон обычно останавливается около 90% DCI-P3. Когда дело доходит до яркости, ЖК побеждает в солнечных комнатах. Фабричные модели легко выходят выше 1000 нитов. Большинство OLED-экранов остаются между 600-800 нитами в течение длительного периода времени.
Посмотреть со стороны показывает большой разрыв. OLED сохраняет одинаковые цвета почти на 180 градусов. Это идеально подходит для командных рабочих станций или общественных киосков. ЖК-экраны начинают выглядеть вымытыми после 85 градусов. ЖК-дисплеи типа IPS лучше, но все же в основном хороши, когда вы сидите прямо впереди. Вот основные моменты:
-
OLED отличается черными уровнями и контрастом для захватывающих впечатлений.
-
OLED поддерживает широкие цветовые гаммы для яркого воспроизведения.
-
OLED обеспечивает последовательное качество с различных углов.
-
ЖК предлагает натуральные цвета с сильной яркостью для окружающего света.
-
ЖК может сменять оттенки вне оси, ограничивая широкие настройки. Эти точки помогают вам выбрать правильную для вашей комнаты и потребностей.
Анализ точности цвета: как LCD и OLED сравниваются
Точность цвета очень важна для работы, такой как рисование, проектирование или чтение медицинских сканирований. Даже мелкие ошибки могут вызвать проблемы. Экраны OLED достигают значений дельта-E ниже 2. Это означает, что цвета остаются очень близки к реальному стандарту, такому как sRGB или Adobe RGB. Никакое подсветление не мешает. Белые и черные остаются чистыми. Это дает плавные градиенты для тренировочных программ или сканирования тела. Органические материалы могут создавать точные длины волн света без дополнительного распространения.
ЖК-экраны зависят от цвета подсветки и качества фильтров. У старших есть дельта-Е около 3-5. Новые квантовые точечные ЖК-дисплеи работают намного лучше. Они приближаются к уровням OLED и остаются стабильными в нормальном свете. Иногда краи выглядят немного оттенченными, потому что подсветка не совсем равномерна. Премиум-модели с FALD исправляют большую часть этого. Для важных работ хорошие ЖК-дисплеи с 10-битным цветом могут показывать 1,07 миллиарда цветов, как и OLED.
В прямых тестах OLED обычно выглядит немного более живым без каких-либо изменений. Но современные ЖК-дисплеи почти так же хороши, когда все настроено правильно. Оба становятся отличными после заводской калибровки. Тем не менее, OLED немного выигрывает, потому что каждый пиксель работает в одиночку. ЖК догнал много и стоит меньше для крупных проектов.
Углубление в соотношение контраста: LCD и OLED Face-off
Контрастное соотношение показывает, сколько разницы существует между самым ярким белым и самым темным черным. OLED может достичь бесконечного контраста. Пиксели просто полностью отключаются. Нет никакого дополнительного свечения. Это делает ночные сцены или специальные автомобильные дисплеи потрясающими. Контент HDR показывает каждую мелкую деталь в тенях.
Нормальные ЖК-экраны остаются между 1000:1 и 5000:1. Подсвет никогда не выключается полностью. Даже при местном затемнении некоторый свет утечет и создает цветение вокруг ярких объектов. ЖК-экраны автомобилей становятся очень яркими для дневного использования, но внутри темных комнат OLED явно лучше. Новые микро-светодиодные фонари подталкивают цифры ЖК-экранов выше, возможно, до 20 000:1 в один день. Сейчас ничего не превосходит настоящий черный пиксель.
К числу ключевых моментов относятся:
-
OLED реализует бесконечные контрасты через выключение на пиксель.
-
Настоящие черные определяют OLED’ с краем в глубине.
-
OLED повышает жизненность в темных условиях.
-
Коэффициенты LCD страдают от врожденных ограничений фонового освещения.
-
Нет истинного черного Марса LCD’ с темным рендерингом.
-
FALD сужает, но не’ t мост разделения. OLED явно выигрывает на рабочих местах, где контраст имеет наибольшее значение. Другие вещи, такие как цена, по-прежнему играют определенную роль.
Оценка срока службы: OLED Vs LCD
Сколько длится экран очень важно для машин, которые работают весь день. Органические части OLED медленно теряют яркость. Период полураспада обычно составляет 30 000-50 000 часов. Синие пиксели износятся быстрее всего. Статические изображения, такие как меню или автомобильные измерители, могут вызвать сгорание. Новое программное обеспечение немного перемещает пиксели и ограничивает яркость. Это может подтолкнуть реальную жизнь до 100 000 часов, если использоваться осторожно.
ЖК-экраны обычно длится 50 000-100 000 часов. Они никогда не горят, потому что кристаллы не органически. Подсветительные светодиоды могут отказаться после 30 000 часов, но их легко изменить. Тяжелые промышленные ЖК-дисплеи работают от -40 ° C до 90 ° C температуры хранения. Короче говоря, LCD более жесткий для тяжелых работ. OLED постоянно улучшается с помощью лучших материалов с каждым годом.
Сравнение энергоэффективности: что экологически чистее, ЖК или OLED?
Потребление энергии является большой проблемой для зеленых продуктов и аккумуляторных устройств. OLED освещает только пиксели, которые нуждаются в нем. Темные изображения могут сэкономить до 30% энергии по сравнению с ЖК. Это помогает телефонам и планшетам продлиться дольше. Когда весь экран яркий, OLED на самом деле использует немного больше энергии.
ЖК поддерживает фоновое освещение все время. Он использует постоянную мощность независимо от того, что показано. Яркие белые экраны эффективны, но темные области по-прежнему тратят энергию. Типичная 10-дюймовая панель использует 10-15 Вт. Умные функции затемнения делают его лучше. Большие экраны делают разницу более ясной. Темные интерфейсы на больших OLED-мониторах много экономят. Оба типа становятся более эффективными с каждым годом.
Сравнение цен: стоит ли OLED дополнительной стоимости по сравнению с ЖК?
Цена зависит от того, насколько трудно их сделать. OLED требует специальных вакуумных машин и редких материалов. Это делает его в 2-3 раза дороже. 15-дюймовый OLED модуль стоит $200-500. Такой же размер LCD стоит $100-200. Фабрики все еще теряют некоторые OLED-панели во время производства, поэтому цены остаются высокими.
LCD-линии работают десятилетиями. Дешево зарабатывают миллионы. Это снижает затраты для заводов и крупных покупателей. Долгая жизнь также экономит деньги позже. OLED стоит дополнительных денег только тогда, когда требуется высшее качество. Для большинства объемных проектов ЖК дает наилучшую стоимость.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
В чем основные различия между LCD и OLED дисплеями?
OLED использует самоизлучающиеся органические материалы для работы без подсветки, обеспечивая истинные черные цвета и высокие контрасты. ЖК модулирует подсветку через кристаллы, предлагая доступность и превосходство солнечного света.
Являются ли OLED-дисплеи более энергоэффективными, чем LCD?
Эффективность варьируется: OLED экономит на темноте путем выключения пикселей; ЖК стабилизирует яркость, но отходы в минимумах.
Почему OLED-дисплеи дороже, чем LCD?
Сложные органические вещества и более низкие урожайности повышают затраты на производство OLED по сравнению с LCD’ зрелых процессов.
Какая технология дисплея лучше для глаз, LCD или OLED?
OLED облегчает низкое освещение через контрасты; ЖК помогает ярко через пик яркости, уменьшая напряжение переменно.
Каков срок службы OLED-дисплея по сравнению с ЖК-дисплеем?
Период полураспада OLED 30 000-50 000 часов с риском сгорания; ЖК выдерживает 50 000-100 000 часов надежно.
Партнер с Kadi Display для премиум-TFT LCD-решений
Как ведущий производитель, поставщик и завод, специализирующийся на высококачественных TFT ЖК-дисплеях, Кади Дисплей предлагает индивидуальные решения для промышленных, медицинских и автомобильных потребностей. С более чем 20-летним опытом, ISO-сертифицированное производство в 10 000 ㎡ Объект в Шэньчжэне и отсутствие настройки MOQ, включая модули высокой яркости до 1100 нитов и широкотемпературные варианты, повышают эффективность проектов. Свяжитесь с командой в sales@sz-kadi.com или 86-13662585086 для обсуждения массового снабжения, прототипов или интеграций сегодня.
Последние блоги и новости
- Пошаговое руководство по освоению MIPI DSI
- Выбор лучшего дисплея для встроенного устройства
- Узнайте о размере и соотношении аспектов промышленного ЖК-дисплея
- Солнечно читаемые дисплеи - самые важные параметры наружных ЖК-дисплеев, которые вам нужно знать
- Руководство по растянутым панелям ЖК-дисплеев: стоимость, установка & Ключевые преимущества
Блог и новости
-
TN против IPS2024-7-9
-
TN против IPS2024-7-9