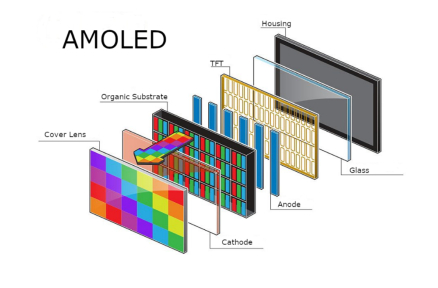
AMOLED (active matrix organic light-emitting diode) and TFT LCD (thin film transistor liquid crystal display) are two distinct display technologies with significant differences in operational principles, performance characteristics, and application suitability. The following outlines the primary disparities between the two technologies, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages:
AMOLED Features, Advantages, and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Self-illuminating Properties: Each pixel of the AMOLED screen is self-illuminating, eliminating the need for a backlight, enabling true black display, and achieving remarkably high contrast.
- High Color Saturation: AMOLED screens deliver more vibrant and vivid colors.
- Fast Response: The self-illumination of pixels results in an exceptionally short response time, making it suitable for fast-moving images and reducing smear.
- Energy Efficiency: When displaying dark or black content, the pixels do not emit light or emit light with low power consumption, contributing to battery conservation.
- Flexibility: AMOLED screens are thinner and possess a degree of flexibility, making them suitable for curved or foldable devices.
- Wide Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is broad, with minimal color and contrast distortion when viewed from different angles.
Disadvantages:
- Cost and Durability: The manufacturing cost of AMOLED screens is relatively high, and early products may have had a shorter lifespan compared to TFT LCDs, although this has improved with technological advancements.
- Risk of Screen Burn-in: Prolonged display of a static image may lead to uneven pixel aging, resulting in the “screen burn-in” phenomenon.
- Color Oversaturation: For professional applications or users with stringent color accuracy requirements, the overly vivid colors of AMOLED screens may not be advantageous.
Characteristics, Advantages, and Disadvantages of TFT LCD:
Advantages:
- Cost-effectiveness: TFT LCD technology is well-established, leading to relatively low production costs.
- Color Accuracy: For applications requiring high color accuracy, such as graphic design, TFT LCD generally offers better color consistency.
- Longevity: TFT LCD screens typically have a long service life and are less prone to pixel aging issues.
- Suitable for Outdoor Use: In brightly lit environments, TFT LCD often provides better visibility than AMOLED.
Disadvantages:
- Requires Backlight: Due to its reliance on a backlight, TFT LCD cannot achieve true black like AMOLED, resulting in a relatively lower contrast ratio.
- High Energy Consumption: Especially when displaying dark content, the backlight remains on, leading to higher overall energy consumption compared to AMOLED.
- Slow Response Time: TFT LCD exhibits a longer response time than AMOLED, potentially resulting in smearing.
- Thickness and Weight: Due to the need for a backlight module, TFT LCD screens are relatively thick and are unsuitable for ultra-thin and lightweight designs.
In conclusion, both AMOLED and TFT LCD technologies have their own unique merits, and the choice between the two depends on specific application requirements, cost considerations, and preferences for display characteristics.
See which size AMOLED (7-15.6 inch)we have:
https://www.kadidisplay.com/product_category/displays-amoled-2/
Latest Blog & News
- What is HMI Screen, Common Uses, Trends and the Future of HMI
- Top Manufacturers of Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Custom Solutions
- Medical Monitors: What Sets Them Apart
- Sunlight Readable Displays – the Key Parameters of Outdoor LCD Displays You Need to Know
- What Are AMOLED Displays: Key Benefits and Applications