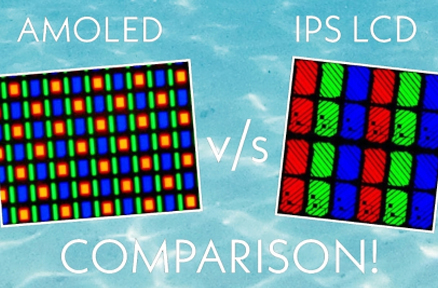
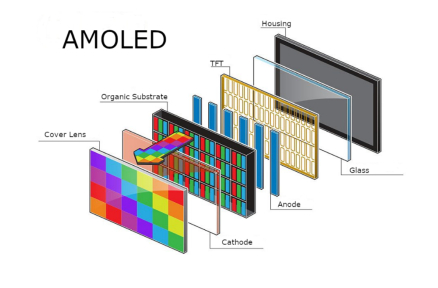
مقدمة إلى PWM (تعديل عرض النبض) للإضاءة الخلفية LED
تعريف PWM
تعديل عرض النبض هو طريقة شعبية لتخفيف الضوء الخلفي LED. يتضمن تحويل LED ON / OFF بمعدل محدد تدرك العين أن LED على بشكل مستمر ولكن عند انخفاض سطوع. هذه الطريقة تستفيد من استمرار العين البشرية في الرؤية لمحاكاة مستويات مختلفة من السطوع عن طريق ضبط مدة بقاء الضوء على خلال كل دورة، المعروفة باسم دورة العمل. يتم تعريف دورة العمل كنسبة من الوقت الذي يكون فيه شيء على مقابل الوقت الذي يكون فيه إيقاف.
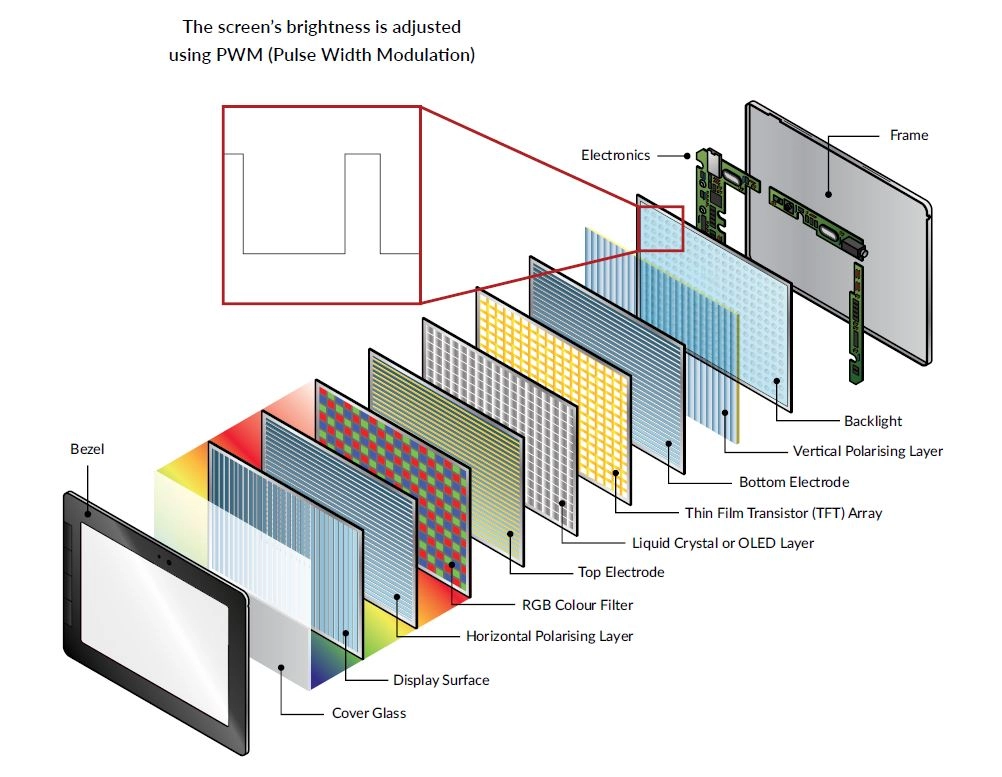
دور PWM في التحكم في الإضاءة الخلفية LCD
هناك العديد من الطرق المتاحة لقيادة الإضاءة الخلفية. واحدة من الأكثر شعبية هي تعديل عرض النبض (PWM). أغلبية شاشات LCD يحتوي على إضاءة خلفية LED (Light Emitting Diode). تسمح PWM بالتحكم الدقيق في هذا الإضاءة الخلفية ، مما يتيح للمستخدمين ضبط مستويات السطوع بفعالية مع تقليل هدر الطاقة. هذا يجعل PWM تقنية أساسية في شاشات LCD الحديثة حيث كل من الأداء والكفاءة مهمة.
مزايا استخدام PWM للتحكم في الإضاءة الخلفية
كفاءة الطاقة
توفر PWM فوائد كبيرة لتوفير الطاقة. باستخدام مخطط تعديل عرض النبض ، يتم تحقيق العديد من المزايا على طريقة الجهد المستمر البسيطة. الميزة الرئيسية هي الكفاءة. على سبيل المثال ، إذا تم تشغيل LED بخمس أضعاف التيار الاسمي لمدة 1/5 من الوقت ، فإن متوسط التيار هو نفسه ، ولكن يمكن تقليل خسائر الطاقة إلى أدنى حد بسبب انخفاض توليد الحرارة والتبديل المثالي.
التحكم في السطوع والتخفيف
PWM تمكن من التحكم في سطوع سلس واسع النطاق. يمكن أيضًا استخدام هذه التقنية لتوفير مستوى سطوع طبيعي للشاشة ولكن عند متوسط تيار أقل لتوفير الطاقة. تعديل نسبة التشغيل / إيقاف يسمح بالتخفيف الدقيق دون المساس بالتوحيد عبر الشاشة. على عكس التخفيف التناظري ، والذي قد يسبب إضاءة غير متساوية عند مستويات منخفضة ، يحافظ PWM على انتاج ضوئي ثابت.
انخفاض استهلاك الطاقة
واحدة من الميزات الرئيسية في الأجهزة التي تعمل بالبطاريات هي انخفاض استخدام الطاقة. يمكن خفض متوسط الطاقة بمعامل 50٪ على الأقل لإنتاج مستوى سطوع متوقع معين. هذا يجعل PWM مثالية للتطبيقات المحمولة مثل الأجهزة اللوحية والشاشات الصناعية المحمولة حيث يوسع توفير الطاقة وقت التشغيل.
عمر العرض الممتد
تساعد PWM على تقليل الإجهاد الحراري على مصابيح LED عن طريق نبضها بدلا من تشغيلها باستمرار في التيارات العالية. هذه العملية المتقطعة تخفض درجات حرارة التقاطع وتطال عمر المكونات ، مما يساهم في وقت حياة طويل (50000 ساعة على الأقل) في شاشات عالية الجودة مثل تلك التي تقدمها Kadi Display.
اعتبارات الأجهزة لـ PWM
متطلبات سائق LED
عادة ما يكون هناك حاجة إلى سائق لمصابيح LED من نوع الضوء الخلفي بسبب المستوى الحالي. لا يمكن تشغيله مباشرة من مخرج رقمي مثل جهاز تحكم صغير. في كثير من الحالات، يتم استخدام FETs على المستوى المنطقي كمشغلين مع مقاومات البوابة المناسبة. لتيارات أعلى وكفاءة أفضل، يمكن استخدام برنامج تشغيل LED من نوع التبديل لتشغيل ضوء خلفي LED لتيارات أعلى وكفاءة أعلى.
استقرار إمدادات الطاقة
يجب أن يضمن تصميم مصدر الطاقة الحد الأدنى من التموج والمساحة الكافية أثناء أحداث التبديل. يصبح الاستقرار أكثر أهمية عند استخدام شاشات عالية السطوع مثل شاشة HDMI الصناعية 1280 * 720 10.1 بوصة من Kadi Display مع 1500 نيت ، والتي تتطلب تنظيمًا ثابتًا للجهد والتيار في ظروف تحميل مختلفة.
أفضل الممارسات في تصميم الدوائر
يجب على المهندسين اتباع ممارسات تخطيط PCB الجيدة بما في ذلك أطوال التتبع القصيرة لمسارات التردد العالي ، ومخططات التأريض المناسبة ، وتقنيات قمع EMI. PCB 100٪ مع عملية الذهب الغمر لضمان مقاومة التآكل القوية، موصلات كهربائية ممتازة وموثوقية اللحام، وضمان أنه حتى تحت التبديل المتكرر، لا تزال سلامة الإشارة سليمة.
اعتبارات البرمجيات الثابتة والبرمجيات
اختيار تردد PWM
عادة ما يتم تشغيل / إيقاف LED بين 60 إلى 240 مرة في الثانية (هرتز). أي أبطأ من 50 هرتز وتدرك العين الومض. ومع ذلك ، قد تؤدي الترددات فوق 1000 هرتز إلى مشاكل EMI أو تقليل كفاءة السائق بسبب خسائر التبديل.
تعديل دورة العمل
تعديل دورات العمل يسمح بالتحكم الديناميكي في السطوع بناء على ظروف الضوء المحيط أو تفضيلات المستخدم. لتنفيذ هذه التقنية، يجب تعيين التيار الذروة في التيار النموذجي المحدد للشاشة ونسبة تشغيل / إيقاف النبضات تختلف من ما يقرب من 100٪ إلى ما يقرب من 0٪ على.
تجنب مشاكل الومض
يمكن تخفيف الوهمة عن طريق اختيار الترددات المناسبة (> 100 هرتز) وضمان آليات توقيت مستقرة في البرمجيات الثابتة. العيب [لـ PWM القائمة على البرمجيات] هو أن هذا يستخدم وقت معالجة أكبر (تكلفة وحدة المعالجة المركزية)؛ على الرغم من أنه، في الممارسة العملية، هو الحد الأدنى. تفضل معظم الأنظمة مؤقتات الأجهزة التي تفرغ المعالجة من وحدات المعالجة المركزية مع الحفاظ على الدقة.
تطبيقات الإضاءة الخلفية التي تدفعها PWM
الإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية
الهواتف الذكية والأجهزة اللوحية وأجهزة الكمبيوتر المحمولة والتلفزيونات تستفيد جميعها من شاشات LCD التي تتحكم بها PWM بسبب حاجتها إلى سطوع قابل للتعديل في ظروف إضاءة مختلفة دون التضحية بعمر البطارية أو الجودة البصرية.
العروض الصناعية
في البيئات الصناعية التي يجب أن تعمل فيها الشاشات بشكل موثوق على مدى فترات طويلة في ظروف قاسية ، تضمن PWM المتانة والأداء. عرض كادي يوفر حلول قوية مثل وحدات التصميم من الدرجة الصناعية التي تتميز بألواح عالية السطوع مع نطاقات درجات حرارة واسعة من -20 درجة مئوية إلى 70 درجة مئوية.
السيارات والأجهزة الطبية
في المركبات أو المعدات الطبية حيث تكون قراءة الشاشة وموثوقيتها مهمة، تقدم PWM التحكم المستقر في الإضاءة مع تلبية معايير EMI الصارمة مثل EN55032 / EN55035. حماية ESD العالية (الهواء ± 8KV / الاتصال ± 4KV) يزيد من تعزيز مرونة النظام في التطبيقات الحساسة.
أسئلة متكررة
س: ما التردد الذي يجب أن أستخدمه لإشارة PWM؟
يجب أن يكون تكرار تردد النبض أكبر من 100 هرتز ولكن ليس أكبر من 1000 هرتز لتجنب الومض المرئي مع تقليل EMI.
س: هل يمكنني قيادة مصابيح LED مباشرة من جهاز التحكم الدقيق الخاص بي؟
لا يمكن تشغيله مباشرة من مخرج رقمي مثل جهاز تحكم صغير. استخدم دائرة السائق المناسبة بدلا من ذلك.
س: كيف يقارن PWM مع التخفيف التناظري؟
يحافظ PWM على توزيع ضوئي موحد حتى عند مستويات سطوع منخفضة على عكس التخفيف التناظري الذي قد يسبب إضاءة غير متساوية بسبب تدفقات القيادة المنخفضة.
س: هل هناك أي خطر من الولمض مع PWM؟
نعم - إذا كان التردد يقل عن ~ 60 هرتز أو إذا كانت آليات التوقيت غير مستقرة - ولكن يمكن معالجة هذا من خلال تكوين الأجهزة الصحيح.
تخصيص حل العرض الخاص بك من Kadi Display
عرض كادي تقدم خدمات تخصيص كاملة مصممة خصيصا لاحتياجات التطبيقات الخاصة بك - من أنواع الواجهة (HDMI / Type-C / MIPI / LVDS) إلى التكامل الميكانيكي مثل خيارات الإسكان أو الغطاء الزجاجي. خدمة تخصيص: نحن نعرض أفكارك! تخصيص FPC والكابل تخصيص الإسكان لتسهيل التجميع تخصيص LCM / TP pinout تخصيص سطوع الإضاءة الخلفية تخصيص الواجهة. ما إذا كنت’ إعادة تطوير نظام مضمن أو شاشة صناعية تتطلب متانة شديدة، كادي لديها مصنع من أكثر من 5000 متر مربع ولها R & amp المهنية؛ فريق D المسؤول عن لوحات محول الإشارة. ميزة PWM الخارجية القابلة للتعديل تضمن التوافق مع متطلبات التخفيف المختلفة عبر الصناعات.اتصل بنا اليوم لأفضل سعر وأفضل عروض.
آخر مدونة وأخبار
- Choosing the Best Display for Your Embedded Device
- Learn About the Industrial LCD Display Screen Size and Aspect Ratio
- Sunlight Readable Displays – the Most Important Parameters of Outdoor LCD Displays You Need to Know
- دليل شاشات LCD الممتدة: التكلفة والتركيب الفوائد الرئيسية
- دليل اختيار LCD 7 بوصة: 800 × 480 إلى FHD شاشة RGB / LVDS / MIPI DSI كادي
مدونة ذات صلة وأخبار
-
TN مقابل IPS2024-7-9
-
TN مقابل IPS2024-7-9