Understanding LCD and OLED Technology
Definition and Basic Principles of LCD
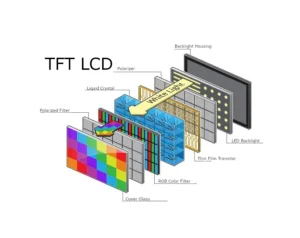
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a type of panel display technology that uses crystals to adjust light levels for creating visual images by controlling the backlight source that shines through colored filters in devices, like TVs and smartphones known for their sharp image quality and widespread use. Here, at Kadi Display, our TFT–LCD collection highlights these features guaranteeing longevity and vibrant color representation resulting in a display quality, for the haul.
Definition and Basic Principles of OLED
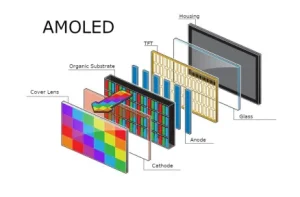
An Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) display is made up of compounds that produce light when electricity passes through them instead of relying on a backlight like LCD screens do. Each pixel creates its light source independently of the others leading to pure black tones by switching off individual pixels which enhances color vibrancy and contrast levels for a more visually appealing viewing experience. Kadi Display also provides screens that use OLED technology to present images, with exceptional clarity.
Visual Performance Comparison
Color Accuracy and Range
When it comes to color accuracy and range, OLED displays generally outperform LCDs. OLED screens provide deeper blacks and a wider color gamut, thanks to their ability to turn off individual pixels. This feature allows for stunningly vibrant colors, which are essential in applications requiring high visual fidelity, such as professional photography and graphic design. Conversely, while modern LCDs, especially those with IPS technology, can offer dependable color reproduction, they often have limitations when it comes to producing true blacks and a dynamic range of colors.
Brightness and Contrast Ratios
OLED displays shine in terms of contrast ratios due to their capacity for absolute blacks, yielding a more engaging viewing experience. High contrast ratios make details in bright and dark scenes more distinguishable. LCDs, while improving in brightness, still depend on backlighting, which can lead to some bleed-through and decreased contrast when by comparison. However, Kadi Display’s advanced IPS TFT LCDs, capable of high brightness and contrast, can maintain excellent visibility even in well-lit environments, making them highly versatile for various applications.
Viewing Angles and Uniformity
The viewing angles of OLED displays are typically superior to those of traditional LCD technology. With an OLED, the display maintains image quality and color fidelity even at sharp viewing angles. In contrast, LCDs, particularly those lacking IPS technology, can suffer from color distortion and contrast loss when viewed off-axis. Kadi Display’s IPS TFT–LCDs provide a significant advantage in this area, offering viewing angles that extend up to 178 degrees without sacrificing clarity and color accuracy.
Motion Blur and Refresh Rates
In terms of motion blur and refresh rates, OLEDs tend to offer faster response times, which is crucial for fast-moving images, such as in gaming or action films. This characteristic significantly reduces blurring effects and allows for a smoother experience. While the response times of LCDs have improved over recent years, they can still lag behind OLED displays, particularly in scenes with rapid motion. Kadi Display’s TFT-LCD solutions feature responsive designs to improve the user experience in high-speed scenarios; however, the inherent technology of OLED may provide users with a preferable option for dynamic content.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Longevity Factors for LCD Displays
LCD screens tend to last than OLED displays because they don’t have self-emitting parts that can cause screen burn-in and deterioration, over time. Kadi Display focuses on durability in its manufacturing methods by following industry norms to ensure that our TFT LCD screens can endure conditions and perform well even after prolonged use. Due, to their build quality and longevity benefits LCD screens are commonly preferred for applications where durability is essential.
Degradation Concerns for OLED Screens
OLED screens provide quality but may face degradation issues due, to their construction materials like organic components that wear out faster compared to LCD parts, especially in high brightness settings leading to burn-in effects where static images linger on the screen affecting visual quality; consumers need to take into account these deterioration factors when selecting an OLED display, especially for uses involving constant images such, as gaming or news feeds.
Power Consumption Efficiency
Energy Usage in LCD Technology
Power usage plays a role, in screen technology with LCD screens known for their energy consumption habits. Their efficiency is mainly attributed to the use of a backlight and the power-saving features found in types of displays. Kadi Display’s TFT LCD screens are crafted with a focus, on energy conservation to ensure they run smoothly while using power. This efficiency not only cuts down expenses but also helps prolong the lifespan of devices that utilize this technology.
Power Efficiency in OLED Displays
However certain situations may witness displays being notably power efficient. In instances where darker images are displayed OLED screens consume power by allowing individual pixels to be switched off. This becomes beneficial, for individuals who favor dark-themed interfaces or applications featuring visuals. Moreover, OLED displays typically exhibit power efficiency in situations requiring color saturation levels. Yet the overall energy efficiency can significantly fluctuate based on usage scenarios and brightness settings.
Environmental Impact
Ecological Footprint of LCD Production
The manufacturing of LCD screens goes through steps that have an impact, on the environment. This includes obtaining and handling materials like crystals and glass substrates and components for backlighting which create waste and use up a lot of energy. Furthermore constructing LCD panels needs an amount of water for cooling and cleaning which enhances their footprint. Companies such as Kadi Display are moving towards methods by improving energy efficiency in their production processes and reducing waste through recycling programs. Moreover utilizing materials and sustainable production techniques can contribute to lowering the environmental effects of LCD manufacturing.
Sustainability Considerations for OLED Manufacturing
OLED technology raises sustainability issues well because of the materials used in its production process; the organic compounds responsible, for generating light, in OLED displays may present difficulties during manufacturing and disposal stages. However, research is being conducted to enhance the sustainability of OLED manufacturing by exploring materials that are more environmentally friendly and establishing methods to efficiently recycle OLED components. In the quest, for friendly options in the business world, today’s focus is, on ensuring that LCD and OLED technologies progress sustainably to reduce their ecological footprint significantly.
Integration with Kadi Display’s Product Lineup
At the cutting edge of display technology innovation is Kadi Display, with a range of products that includes LCD and AMOLED displays in their lineup. They specialize in providing top-notch TFT LCDs featuring IPS technology to offer clients color accuracy and broad viewing angles. Ideal for applications that demand longevity and energy conservation these TFT LCDs, from Kadi Display stand out for their performance. Kadi Display’s AMOLED lineup allows customers to utilize the benefits of technology, like color display and deep blacks that are perfect, for multimedia usage scenarios. Their diverse selection enables clients to pick display options that suit their requirements while enjoying Kadi Display’s dedication to top-notch quality and durability.
Making an Informed Decision between LCD and OLED
When determining whether to invest in LCD or OLED technology, it is essential to consider several factors, including application requirements, budget constraints, and desired visual quality. Those in fields where color accuracy and contrast ratios are critical—such as graphic design or videography—may find that OLED displays provide the superior performance necessary for their work. Conversely, for applications involving static imagery, such as digital signage or user interfaces, LCDs may offer a practical solution with their resistance to burn-in and longer longevity. Ultimately, the choice between LCD and OLED will depend on a careful assessment of individual needs and preferences, balancing factors such as image quality, energy consumption, manufacturing sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
Customers can further explore Kadi Display’s product offerings to find tailored solutions that meet their specific display requirements. The company’s expertise in both TFT-LCD and OLED technologies ensures that clients can identify and implement the most suitable display while benefiting from Kadi Display’s commitment to innovation and quality in their product development processes. Through comprehensive support and an extensive product lineup, Kadi Display empowers customers to make informed decisions for optimal display performance across a multitude of applications.