Wat zijn Embedded Displays
Definitie en kernkenmerken
Een ingebedde weergave is een schitterend scherm ingebouwd rechtstreeks in een elektronisch gadget. Het wordt geleverd met een eigen controller om info te tonen en te werken met de functies van het apparaat. Dit zijn geen standalone monitors. Ze maken deel uit van de belangrijkste taak van de gadget.
Het scherm en de hersenen van het apparaat zijn super strak, vaak delen delen delen zoals de controller. Ze kunnen eenvoudige cijfers of schitterende afbeeldingen tonen. Bovendien hebben veel van hen touchfuncties voor leuke, hands-on controle.

Hoe embedded displays verschillen van traditionele displays
Regelmatige displays zijn als externe add-ons. Ze hebben hun eigen stroom en video aansluitingen nodig. Embedded displays zijn echter veel compacter en ingebouwder. Ze zijn robuust en betrouwbaar voor ruwe plaatsen. Omdat ze deel uitmaken van het gadget, praten ze snel met andere onderdelen, met minder vertraging en betere energiebesparing.
Belangrijkste componenten van een Embedded Display System
Display Panel Technologies Gebruikt in Embedded Systems
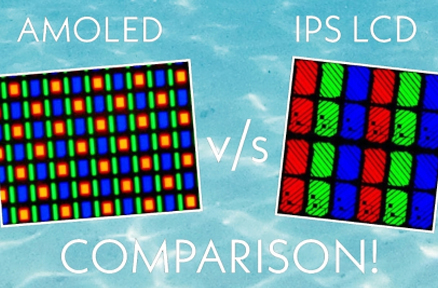
LCD-, OLED- en E-Ink-panelen
Embedded systemen gebruiken verschillende schermtypen op basis van wat nodig is:
-
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)Super gebruikelijk omdat ze goedkoop zijn en in alle maten zijn verkrijgbaar. IPS LCD's hebben brede kijkhoeken tot 178 graden, waardoor kleuren helder en helder blijven vanaf bijna overal.
-
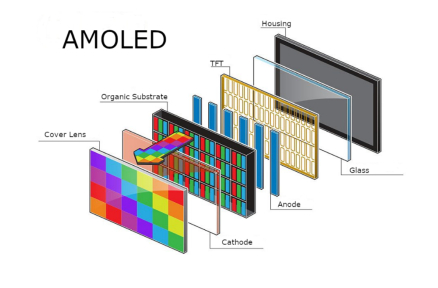
OLED (organische lichtemitterende diode): Perfect voor zappy kleuren en diepe zwarten. AMOLED-schermen kunnen afzonderlijke pixels uitschakelen voor echte donkere niveaus.
-
E-InktGebruikt in e-readers of low-power gadgets omdat ze nauwelijks stroom drinken voor stille beelden.
Geïntegreerde Touch Interfaces
Capacitieve vs. Resistieve Touch Technologies
Touch maakt het gebruik van gadgets veel leuker:
-
Capacitieve TouchSuper gevoelig en ondersteunt multi-touch. Je zult het zien in telefoons en fancy embedded systemen.
-
Resistieve TouchWerkt als je twee lagen bij elkaar drukt. Het is geweldig voor moeilijke plekken waar mensen handschoenen dragen, zoals fabrieken.
Veel ingebouwde schermen hebben aanraking, waardoor u op het scherm kunt tikken om dingen te beheren. Ontdek de touchopties van Kadi Display.
Embedded Controllers en Processing Units
Een volledig ingebedd display systeem heeft een paar sleutelbits:
Op zijn eenvoudigste zijn er vier delen: Display Glass, Display Controller, Framebuffer, Microcontroller.
-
De Vertoningsglas toont foto's op basis van pixel info.
-
De Display Controller stuurt pixelgegevens vanuit de framebuffer.
-
De Framebuffer bevat pixel kleur info.
-
De Microcontroller updates alleen de delen van de framebuffer die veranderen wat op het scherm staat.
De microcontroller hoeft het hele scherm niet opnieuw te maken. Het tweakt gewoon wat anders is dan voorheen.
Toepassingen van Embedded Displays in verschillende industrieën
Industriële automatisering en besturingssystemen
Embedded displays zijn een grote zaak in Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI). Ze laten werknemers processen in real-time zien met coole afbeeldingen. Ze zijn sterk genoeg voor ruwe plaatsen zoals superhete of schubbelende fabrieken.
Consumentenelektronika en slimme apparaten
Slimme huishoudelijke spullen, zoals thermostaten of koelkasten, gebruiken ingebouwde touchdisplays voor eenvoudige bediening. Deze systemen zijn klein, snel en zien er glad uit.
Automotieve instrumentatie en infotainmentsystemen
Auto's gebruiken ingebouwde displays voor digitale dashboards, muziekconsoles, navigatie en klimaatbeheersing. Ze combineren vaak capacitieve touchscreens met klikkende feedback.
Interfaces voor medische apparatuur
In medische apparatuur zoals draagbare echomachines of patiëntenmonitors tonen ingebedde displays real-time informatie. Ze blijven schoon en voldoen aan de hygiëneregels met afgesloten touchscreens.

Voordelen van het gebruik van embedded displays
Voordelen van ruimtebesparing en integratie
Embedded displays zijn supercompact in vergelijking met externe schermen. Ze snijden rommelige draden, kijken netjes en werken betrouwbaar.
Verbeterde gebruikersinterface mogelijkheden
Met zippy microcontrollers of grafische chips kunnen ontwikkelaars coole, aangepaste dashboards maken die precies passen aan wat gebruikers nodig hebben.
Verbeterde betrouwbaarheid in zware omgevingen
Deze displays zijn sterk gebouwd voor ruwe plekken zoals schubbende of stofige plaatsen. Ze blijven een lange tijd goed werken.
De rol van Embedded Touch Displays in moderne interfaces
Interactiviteit verbeteren met Touch-functionaliteit
Multi-Touch-mogelijkheden en gebaarherkening
Moderne ingebouwde touchdisplays laten je leuke dingen doen zoals knijpen om te zoomen of veegen. Deze zijn belangrijk voor telefoons, medische apparatuur of autosystemen.
Interactie
Veel ingebouwde displays hebben touch, waardoor saaie schermen worden omgezet in levendige bedieningspanelen.
Verbetering van de gebruikerservaring door naadloze integratie
Ingebouwde ontwerpen laten bedrijven soepele interfaces maken. Het display blendt in het gadget zonder uit te steken, waardoor het zowel nuttig als mooi is.
Aangepaste Embedded Display van Kadi Display
Kadi weergave gaat het allemaal om aangepaste embedded display oplossingen. Ze bieden LCM (Liquid Crystal Module), TP (Touch Panel), PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly), bindingsdiensten, signaaladapterplaten en aluminium of metalen behuizingen - allemaal gemaakt om te passen aan wat klanten willen.
Ze zijn allemaal betrokken bij het maken van unieke LCM / TP / PCBA-setups om uw producten op te vallen en de ontwikkelingstijd te verkorten. Hun spullen omvatten:
-
Aangepaste cover glas: Kies vorm, logo, kleur of dikte.
-
Aanpassing van achtergrondverlichting: Tweak helderheid of dikte.
-
Interface opties: TTL/LVDS/MIPI/EDP/HDMI/VGA/USB-A.
-
Optische binding: Gebruikt heldere lijm om luchtgapen te knippen, waardoor zichtbaarheid wordt verhoogd.
Kadi's hoge helderheid IPS TFT LCD's bereiken tot 2500cd / m² helderheid. De meeste van hun heldere schermen gaan over 800cd/m², sommige zelfs tot 2500cd/m². Dit maakt ze super helder in helder licht, perfect voor buiten- of fabrieksgebruik. Krijg jouw bij Kadi Display.
Veelgestelde vragen
Wat maakt een embedded display anders dan een standaard monitor?
Een ingebouwd display is direct ingebouwd in een gadget. Standaardmonitoren zijn apart en hebben hun eigen aansluitingen nodig.
Kunnen embedded displays multi-touch functies ondersteunen?
Ja! Veel moderne ingebouwde touchdisplays hanteren multi-touch en coole gebaren zoals zoomen of veegen.
Zijn aanpassingen beschikbaar voor industriële toepassingen?
Totaal! Kadi Display past dekglas en behuizingen aan voor eenvoudige montage in moeilijke industriële installaties.
Welke soorten interfaces ondersteunen de embedded modules van Kadi?
Ze hebben tal van opties: TTL/LVDS/MIPI/EDP/DP/HDMI/Type-C/VGA/USB-A. Deze werken met allerlei systemen.
Hoe verbetert optische binding de prestaties?
Optische binding vermindert luchtgaten, waardoor schermen in helder licht gemakkelijker te lezen zijn en stof of water buiten houden.
Laatste Blog & Nieuws
- Een stap-voor-stap gids voor het beheersen van MIPI DSI
- Het beste scherm kiezen voor uw embedded apparaat
- Lees meer over de schermgrootte en aspect ratio van het industriële LCD-scherm
- Zonlicht leesbare schermen - de belangrijkste parameters van buiten LCD-schermen die u moet weten
- Gerekte Bar LCD Displays Gids: Kosten, Installatie & Belangrijkste voordelen