In the realm of display technologies, AMOLED and LCD represent two significant types that cater to various user preferences and device requirements. This comprehensive guide aims to dissect the technical details, performance aspects, and notable products associated with each display type. By delving into the intricacies of AMOLED and LCD technologies, advanced users will be equipped to make informed decisions based on their specific display needs.
Introduction to Display Technologies
Brief Overview of Display Types
There are tons of display technologies available out there but the very common ones are AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). Both have made huge strides on devices from smartphones and televisions to laptops and monitors. LCD has been a de-facto choice for years with affordable pricing and higher availability which makes it a popular one, but AMOLED started making inroads with vivid colours and deep blacks. Advanced users who want to get the best performance out of their displays need to understand the differences in what these technologies can do.
Technical Breakdown of AMOLED Displays
Structure and Functionality of AMOLED
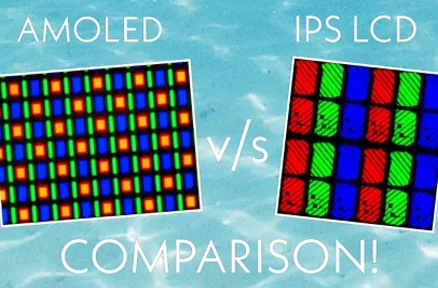
AMOLED displays are a fundamentally different type of design than traditional LCDs. It uses organic material that lights up when an electrical current flows through it. In AMOLED display, there is an independent glow of pixels which provides great colors and black color as well where black is displayed by turning off a pixel completely. Not only does this improve contrast but also enables energy-saving function when darker screens are in use. In contrast, LCDs need a backlight that is turned on no matter what colors the image contains, making them inefficient in that sense.
Performance Characteristics
AMOLED displays stand out in the evaluation of performance by their high contrast ratios and fast response times. This can add to the overall experience, particularly for multimedia applications, as they provide superior color reproduction. AMOLED screens are characterized by more saturated colors, whereas on LCDs we have a calmer palette. But the other big contributor there is viewing angles — AMOLED displays keep quality at any angle you view, one of the bigger advantages over most of those traditional, lower-end LCD panels. Additionally, AMOLED tends to have improved power efficiency for visualizing dark images, thus increasing battery life in mobile devices.
Notable Products: Kadi Display AMOLED Panel
One noteworthy product embodying the advancements of AMOLED technology is the Kadi Display AMOLED Panel. This panel exemplifies the integration of high brightness and exceptional contrast, making it suitable for a range of applications from high-end smartphones to cutting-edge televisions. The panel boasts fast response times, making it especially advantageous for users involved in gaming or fast-moving video content. Coupled with its ability to deliver true black levels, the Kadi Display AMOLED panel stands out in a crowded market of display technologies, catering to professionals and enthusiasts alike who seek enhanced visual performance.
In-depth Analysis of LCD Technology
Fundamentals of LCD Panels
LCD is a cool tech that utilizes liquid crystals and backlighting to function. The basic concept of an LCD is that when you pass a current through a liquid crystal, it rotates light. By using this, we can control the amount of light that is allowed to pass through and make images appear on a screen. Each pixel in an LCD is made up of three subpixels, one for each of the three primary colors: red, green, and blue color; when combined they create all visible colors known to humankind. A backlight technology (like LED) can also impact the performance of an LCD substantially, improving both brightness and color accuracy.
Key Features of IPS TFT-LCDs
IPS stands for the upgraded type of LCD technology. The main benefit over conventional twisted nematic (TN) panels is wider viewing angles. This is essential for work environments when you need multiple users to view the same content, as it ensures color fidelity and contrast are preserved even from extreme viewing angles. Also, since they’ve improved the liquid crystal alignment IPS TFT-LCDs typically provide better color reproduction. This is especially useful in photo-editing applications, graphic design, and other visual media.
High Brightness in LCDs
High-brightness LCDs are meant for outdoor or high ambient light use and overcome many challenges associated with brightness. Such brightness levels on these displays can go above 800 cd/m² and in some cases up to even 2500 cd/m². This ensures that content is visible and crisp even under direct sunlight, which is particularly important for industrial applications as well as outdoor signage. For that, the great contrast present in this type of display helps to bring image details because it is easier to tell apart small changes in brightness and color, thus providing a more pleasant experience for users.
Quality Control Measures: AOI Inspection
The LCD panel manufacturers require quality control in every aspect to make sure that it performs at the highest level and reliability during the product lifespan. This part of the process also includes Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), which is more than just a few visual inspections for manufacturing defects such as pixel failures or alignment. AOI is used to ensure that conductive particles (e.g., dust) are within tolerable limits during the TFT LCD manufacturing process. This inspection process ensures that each display passes defined criteria standards thus reducing the probability of failure once fielded.
Featured Products from Kadi Display
Kadi Display has earned a strong reputation for delivering high-quality LCD panels featuring cutting-edge technology. Their offerings include customizable solutions that allow clients to specify requirements such as logo placement, cover glass finish, brightness levels, and even touch functionalities. Specializing in high-performance LCDs, Kadi Display also focuses on sectors that demand durability and reliable operation, including medical applications and industrial settings. By maintaining rigorous quality assurance processes and leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques, Kadi Display continues to establish itself as a leading provider of LCD technologies.
Comparative Analysis: AMOLED vs LCD
Visual Performance Metrics
AMOLED screens are often celebrated for their ability to provide true blacks by powering off individual pixels, and AMOLED black is named among display characterization standards in visual performance metrics. As a result, the contrast ratio is usually miles better compared to LCDs — since the backlighting is always on at least some level then blacks are more likely to be washed out. AMOLED displays do tend to perform better in color vibrancy since each pixel is independent and can emit its light, giving it a deeper saturation and dynamic range. On the other hand, LCDs (particularly IPS-based) are more uniform in colors and brightness at different angles but cannot achieve very deep blacks, close to what AMOLED screens can do.
Energy Consumption Profiles
Energy consumption is one of the key aspects when it comes to the efficiency of a device, especially for mobile applications. Compared with other displays, AMOLED screens allow for greater power savings while displaying dark themes because individual pixels can be turned off completely, which consumes no energy. This feature is especially useful on power-sensitive devices like smartphones, where battery life is king. In contrast, the energy consumption of LCDs is constant because backlit on full-time regardless of the content displayed. That said, modern LCDs have made significant efficiency advances from improvements in LED backlighting, giving them a fighting chance against power use competition (especially with bright images).
Durability & Longevity Considerations
The durability and longevity of display technologies may greatly impact the end-user experience and lifetime of a product. LCDs usually have a sturdier construction and make for better resiliency against wear and tear than AMOLED displays. This sturdiness is because of the LCD panel’s solid structure that makes them immune to the forceful hits. However, AMOLED screens can suffer from burn-in, which is where static images remain burnt into the display even after they are no longer shown; but they do offer better quality in return. This resilience difference is critical when considering long-term use in diverse environments.
Customization Flexibility with Kadi Display Services
Customization is a critical feature of next-generation display technologies that empower manufacturers and ensure a positive user experience across many types of applications. Kadi Display specifically differentiates itself by offering nearly all custom functionalities for its LCD products; this comprises your choice of interface, from TTL to LVDS to MIPI to HDMI and so on. They also adjust the backlight and design the housing in a way that will be more convenient to put together and use within a larger system. Not only does this enable businesses to make full use of the display technologies that fulfill their operational requirements, but it also ensures high levels of functionality and toughness.
Practical Applications and Market Trends
Industry Use Cases for AMOLED
AMOLED technology offers a wide variety of applications, especially in the consumer electronics field including smartphones and high-end televisions where bright visuals create effective interaction between users and displays. AMOLED displays are also appreciated by the gaming industry, thanks to excellent response times and natural color saturation that further paves the way for a more immersive experience. Wearables like smartwatches utilize AMOLED tech to show bright and visible displays in different environments without hogging the battery. This versatility in applications reflects the increasing prevalence of AMOLED within contemporary technologies.
Common Uses for LCDs
Conversely, LCDs are still widely used in several domains for their reliability and cost-effectiveness. They are often used in computer displays, television sets, and devices requiring consistent performance. High-brightness LCDs, for example, are commonly used in outdoor signage and control systems where visibility needs to be maintained in direct sunlight. Additionally, LCD technology is also used in diverse industries starting from healthcare to automotive as medical displays and infotainment systems respectively, proving the wide-ranging nature and necessity of LCDs in today’s tech-savvy world.
Latest Blog & News
- What is HMI Screen, Common Uses, Trends and the Future of HMI
- Top Manufacturers of Stretched Bar LCD Displays for Custom Solutions
- Medical Monitors: What Sets Them Apart
- Sunlight Readable Displays – the Key Parameters of Outdoor LCD Displays You Need to Know
- What Are AMOLED Displays: Key Benefits and Applications